“Historia del Aloe Vera” - (Una planta mágica)
La planta de Aloe Vera se conoce y se utiliza desde hace siglos. Es un verdadero regalo de la naturaleza.
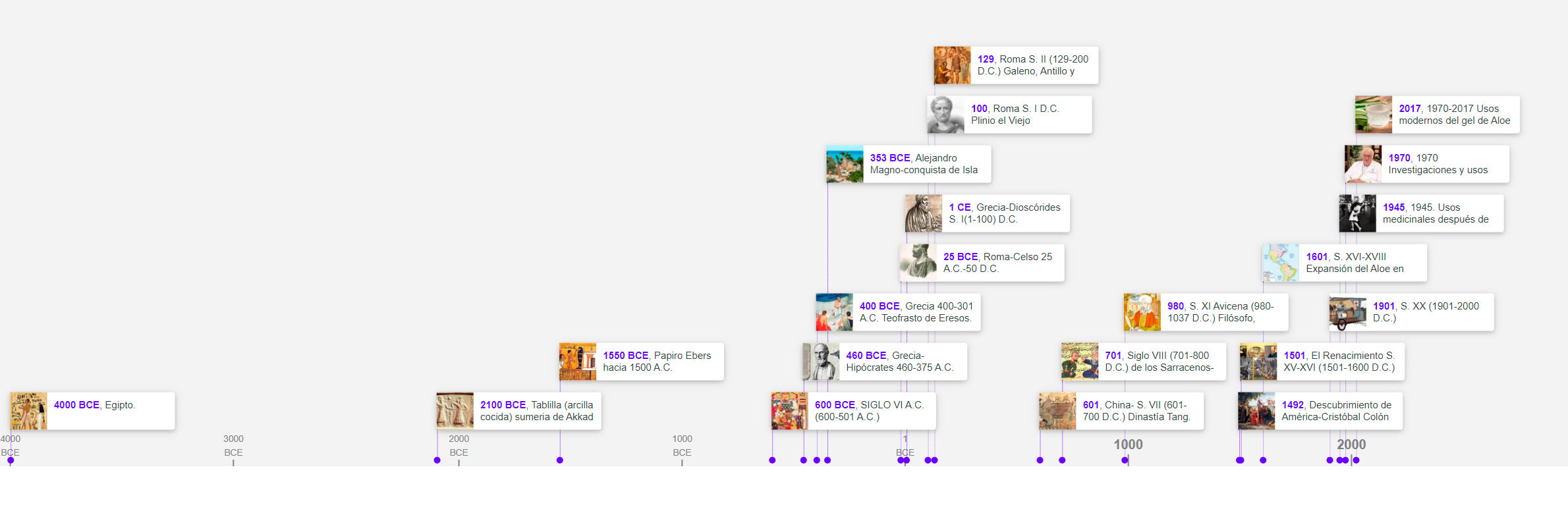
Los registros muestran que los beneficios del Aloe Vera se conocen desde hace siglos por sus ventajas terapéuticas y propiedades curativas. Muchas obras antiguas, incluida la Biblia, se refieren al uso de Aloe. Tallas de 6000 años de las plantas de Aloe Vera fueron descubiertas en Egipto. Fue considerada la "Planta de la inmortalidad" y se ofreció como obsequio de entierro a los faraones fallecidos. Hace 2000 años, el científico griego consideraba al Aloe Vera como la panacea. El uso medicinal del Aloe ya se mencionó hace más de 4000 años en una colección de
Tablillas de arcilla sumeria fechadas en el 2100 a.C. La primera discusión detallada sobre el valor medicinal del Aloe se encuentra en el papiro Ebers, un documento egipcio escrito alrededor de 1550 a. c. La Reina egipcia Nefertiti y Cleopatra lo usaba como parte de sus regímenes de belleza habituales. Alejandro Magno y Cristóbal Colón lo usaron para tratar las heridas de los soldados. Celsius, Dioscórides, Plinio el Viejo y muchos otros escritores han descrito las propiedades del Aloe Vera en sus libros. Ahora el Aloe Vera se cultiva en muchas partes del mundo con clima cálido.
Crece principalmente en la región seca de África, Asia, Europa y América. En la India se encuentra en Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu y LAS ISLAS CANARIAS. Los nutrientes que componen el Aloe Vera son únicos y tienen sorprendentes propiedades curativas naturales. Sus usos son múltiples y sin duda un regalo de la naturaleza a la humanidad.
Nos queda presentarlo a nosotros mismos y agradecer a la naturaleza por su regalo interminable.
I. INTRODUCCIÓN
La historia nos ha demostrado que el Aloe Vera es una de las plantas mencionadas más antiguas de la que se tiene constancia debido a sus propiedades medicinales y beneficios para la salud. Los médicos antiguos lo consideraban una bendición para la humanidad. A menudo llamada la “planta milagrosa” o el “curandero de la naturaleza”, el Aloe Vera es una planta de muchas sorpresas.
Pertenece a la familia Asphodelaceae (Liliaceac). El nombre "Aloe" es derivado de la palabra árabe "alloeh" o la palabra hebrea "halal", que significa sustancia amarga y brillante; "Vera" en latín significa "real". Debido a su sensación de cactus, el Aloe a menudo se llama erróneamente "cactus del desierto". Hay más de 400 especies de Aloe cultivada en todo el mundo, pero es la planta de Aloe barbadensis miller (Aloe Vera o "True Aloe") que ha sido de mayor utilidad para la humanidad debido a las propiedades medicinales que exhibe.

II. HISTORIA DE ALOE VERA
El aloe vera es PLANTA favorita de muchas naciones del mundo. Se ha encontrado y descrito en escritos en muchas culturas diferentes y desde las épocas griega, egipcia y romana. Las referencias también se han encontrado en escritos de las primeras culturas india y china. Ha sido una de las plantas más usadas, buscadas y utilizadas a lo largo de la historia. Muchas obras antiguas, incluida la Biblia, se refieren al uso de Aloe Vera.
La Biblia menciona sacar a Cristo de la cruz y envolver su cuerpo en áloes y mirra (Juan 19: 39).
Encontramos al Aloe Vera apareciendo en todas las fases de la historia con numerosos testimonios de sus grandes valores medicinales.
La historia evolutiva del género Aloe es poco conocida. El Aloe Vera en sí es particularmente misterioso; se ha trasplantado tan ampliamente en todo el mundo por razones comerciales que la ubicación de su hogar ancestral es un tema de debate. Sudán o la península arábiga se han sugerido basándose en similitudes con las especies de Aloe nativas de estas regiones, pero también se han propuesto ubicaciones mucho más lejanas, como las Islas Canarias. Una coalición internacional de científicos del Reino Unido, Dinamarca, Noruega, Australia, Etiopía y Sudáfrica, dirigido por Olwen Grace de Kew Gardens de Londres y Nine Ronsted de la Universidad de Copenhague, han intentado resolver este argumento.
El investigador reunió el muestreo genético más completo del género Aloe producido hasta ahora. Utilizando ADN nuclear y plásmido recién secuenciado y una cantidad sustancial de secuencias preexistentes almacenados en GenBank, interrogaron la relación evolutiva entre los áloes.
La Península Arábica donde el Aloe muy evolucionado está cerca de rutas comerciales históricamente importantes entre Asia y el Mediterráneo. Las fuentes históricas sugieren que el Aloe trazó rutas comerciales de Vera estando bien establecidas en el Mar Rojo y la región del Mediterráneo desde el siglo IV.
ANTES DE CRISTO. Así, la planta de Aloe Vera ha sido conocida y utilizada durante siglos por sus propiedades en salud, belleza, medicina y cuidado de la piel.
La primera nota de aloe vera se encuentra en la tablilla de arcilla sumeria que data del 2100 a.C. y era encontrado en la ciudad de Nippur. La tableta se ha creado en la época del Rey de Akkad y se habla de las propiedades medicinales de esta planta. La primera discusión detallada sobre el valor medicinal del Aloe es probablemente la que se encuentra en el papiro Ebers, un documento egipcio escrito alrededor de 1550 a. C. Este documento da doce fórmulas para mezclar Aloe con otros agentes para tratar trastornos humanos tanto internos como externos. (Samuel y Ria).
El registro más antiguo del uso de Aloe Vera proviene de los egipcios. Hay registros de los egipcios haciendo dibujos de plantas de Aloe Vera en las paredes de los templos. Muchas culturas, como la egipcia, incluso han elevado la planta a un estado "parecido a un dios". Las propiedades curativas del Aloe Vera se utilizaron para siglos ganando el nombre de “Planta de la Inmortalidad”. (Gertrude Baldwin).
La planta de Aloe Vera y sus productos derivados han jugado un papel importante en la medicina y la salud ya en el siglo IV a.C. cuando los antiguos doctores griegos obtuvieron aloe de la isla de Socotra en el Océano Indio. También hay muchas historias al respecto, que las reinas egipcias Nefertiti (1353 a.C.) anunciaron como "la mujer más bella que jamás haya vivido" y la reina Cleopatra VII (69-30 a. C.) la utilizó como parte de su regímenes de belleza y medicinas regulares. Supuestamente Alejandro Magno en 333 a. C. fue persuadido por su mentor Aristóteles para capturar la isla de Socotra en el Océano Índico por sus famosos suministros de Aloe, necesarios para tratar sus soldados heridos. La antigua civilización de Kemet en el valle del Nilo ("Tierra de los negros" ahora conocida como Antiguo Egipto que derivó del nombre griego Aigyptos más tarde latinizado bajo el dominio romano a Aegyptus que derivado del nombre "Hekaptah" que significa "Tierras del templo de Ptah") utiliza Aloe ara medicina tratamientos, cuidados de belleza y embalsamamiento (Manvitha y Bidya, 2014).
El rey Salomón (971-931 a.C.) valoró mucho las propiedades medicinales de esta planta, incluso cultivó su propio aloe vera. En el Salmo 45: 8 encontramos lo siguiente, "Tu ropa huele a mirra, aloe y canela ......." (Svetlana Pasaric).
El aloe vera había viajado a Persia y la India hacia el año 600 a. C. por los comerciantes árabes. Los árabes llamaban Aloe el "Desert Lily" para sus usos internos y externos. Descubrieron una forma de separar el gel interno y la savia de la corteza exterior. Con los pies descalzos aplastaron las hojas y luego metieron la pulpa en las bolsas de piel de cabra. Luego, las bolsas se ponían al sol para que se secasen y el Aloe se convertía en polvo (Gertrude Baldwin).
En la cultura china, el aloe vera ha sido un ingrediente importante en los tratamientos médicos desde los tiempos de Expediciones Marco Polo. El libro de tratamiento de Shi Shen describió al Aloe Vera como el "Método de la Armonía": la planta jugó un papel importante en la vida cotidiana de los chinos. La cultura japonesa también valora mucho la planta. En Japón se la conocía como la "planta real", el jugo se consumía como elixir y los samuráis la usaban para bordados. El pueblo hindú pensó que el Aloe Vera crecía en el Jardín del Edén y lo llamó el “Sanador silencioso”. Los rusos llamaron al Aloe Vera "el elixir de la longevidad". Los indios nativos americanos usaban Aloe por sus poderes emolientes y rejuvenecedores.
En sánscrito, Aloe se conoce como Ghrita Kumari, Kumar significa niña y se creía que esta planta suministró la energía de la juventud a las mujeres y tuvo un efecto rejuvenecedor sobre la naturaleza femenina. En la cultura hindú, la planta de Aloe Vera conserva un lugar importante entre las plantas sagradas del Atharva Veda, donde recibe su nombre - “El sanador silencioso”. Ayurveda (la antigua ciencia india de la salud y la vida considera que el aloe es "Vera rasayana" - el rejuvenecedor del organismo. Según el Ayurveda, el Aloe Vera contiene cuatro sabores: dulce, ácido, amargo y astringente (Svetlana Pasaric). En la medicina ayurvédica, también se aplica en numerosas aplicaciones tales como remedios rejuvenecedores, para problemas de menorrea y para estabilizar el sistema cardiovascular. El aloe es considerada como la planta del equilibrio entre pitta, Kapha y Vata, el Aloe es una de las pocas plantas que tienen estas cualidades. Dioscórides obtuvo la mayor parte de su conocimiento sobre el Aloe Vera viajando con los ejércitos romanos. Escribió por primera vez sobre él en su "De Medica" en 41-68 A.D. Su comentario usa Aloe Vera para furúnculos, curación del prepucio, la piel seca calmante que pica, los genitales ulcerados, las amígdalas, las irritaciones de las encías y la garganta, los hematomas y para detener heridas sangrantes. Pliney el Viejo, un médico del 23 al 79 d.C., confirmó en su 'Historia natural descubrimientos de Dioscórides. La primera referencia al Aloe Vera en inglés fue una traducción de John Goodyew.
1655 A.D. del tratado médico Dioscórides - "De Materia Medica" (Davis, RH).
En el siglo VII, la Materia Médica china escribió sobre el uso del Aloe Vera para la sinusitis y otras pieles. "En el siglo XV, una época que presagió una explosión masiva en la exploración por parte de los líderes en ese momento potencias marítimas, a saber: España, Portugal, Holanda, Francia y Gran Bretaña, fueron los sacerdotes jesuitas de España quienes fueron fundamentales para devolver el Aloe Vera al Nuevo Mundo, como lo llamaban”. Muchos dan crédito a los españoles por traer Aloe Vera no solo al Nuevo mundo, sino también a Centroamérica, West Indies, California, Florida y Texas.
Las primeras misiones españolas tenían padres que administraban las ayudas curativas. Algunos padres llevaban una planta de aloe vera hasta 50 millas para consolar a los enfermos. Los áloes siempre se encontraban en los patios de la misión. Durante el Segundo viaje de Cristóbal Colón a América en 1494, una carta fue escrita por su médico, el Dr. Diego Alverez Chanca, dijo, "Una especie de Aloes que usamos los médicos está creciendo en Hispaniola", dijo una vez Cristóbal Colón, “Cuatro verduras son indispensables para el bienestar del hombre: el trigo, la uva, la aceituna y el aloe. La primera lo nutre, el segundo levanta su espíritu, el tercero le trae armonía y el cuarto lo cura”.
El aloe vera perdió su poder de curación cuando comenzó a importarse. La pulpa funcionó mejor cuando Fresca. Esto perjudicó la reputación del Aloe Vera en la comunidad médica. Los profesionales de Medicina de Europa y América del Norte dejó de usar Aloe Vera y lo reemplazó con drogas. Los científicos determinaron que el proceso de oxidación obstaculizó las propiedades curativas del Aloe Vera. Hizo que la planta perdiera calidad y efectividad, gradualmente lo que lleva a su pérdida de popularidad en áreas donde no se cultiva. En la década de 1950, muchas técnicas de procesamiento fueron intentaron pero fallaron debido al sobrecalentamiento.
Sin embargo, en 1964, el Dr. Bill C. coactiva a un farmacéutico en ejercicio en Dallas, Texas, EE. UU., Se convirtió en un hombre con un sueño: hacer que los beneficios completos del Aloe Vera estén disponibles para el mundo y los millones de personas que necesito. Convencido de que el "gel" de la planta se puede extraer y utilizar sin perder su potencia, el Dr. Coates se dedicó a aprender los secretos de la química de la planta y a hacer lo que nadie había podido hacer jamás en las plantas más de 4100 años de historia conocida - para extraer y estabilizar naturalmente el "Gel" conservando su potencia curativa natural, y en 1968 lo logró (Manvitha y Bidya, 2014). En la década de 1970 había avance en las técnicas de procesamiento y con éxito; estabilizó el gel de la hoja mediante el uso de ingredientes naturales y prensado en frío. También encontraron una forma de separar la cáscara y la aloína. Estas nuevas técnicas de procesamiento encontradas han creado un nuevo mercado para el Aloe Vera. Desde entonces, se han abierto nuevas fronteras para el uso de los estabilizados.
Gel de aloe vera en medicina, atletismo, salud y belleza, cosmética y cuidado animal.
Ahora el Aloe Vera se cultiva en muchas partes del mundo con clima cálido. El aloe vera se usa ampliamente en productos para el cuidado personal, cosméticos, detergentes y es popular como suplemento dietético. Actualmente, las ventas respaldan un negocio multimillonario en todo el mundo. Durante miles de años, el Aloe Vera fue parte del mito y leyendas, pero hoy juega un papel para ayudar a mejorar la salud y la nutrición. La composición de nutrientes del Aloe Vera es una de una clase y tiene increíbles propiedades curativas naturales. Hoy en Japón, el Aloe Vera se usa comúnmente como ingrediente en yogur disponible comercialmente. También hay muchas empresas que producen bebidas de Aloe Vera.. Los habitantes de Tamil Nadu, un estado de la India, a menudo preparan un curry con aloe vera que se lleva consigo con pan indio (pan Nan) o arroz.
Así, el Aloe Vera actuó como un antiguo remedio natural que es definitivamente superior a muchas drogas sintéticas y podría llamarse "Plantas milagrosas modernas".

III. CONCLUSIÓN
El aloe vera es una hierba favorita de muchas naciones del mundo. La planta de Aloe Vera y su derivado.
Los productos han desempeñado un papel en la medicina y el cuidado de la salud desde el siglo IV a. C. Mediante comercio humano y migración, esta planta llegó a ser conocida en todo el mundo. El aloe vera es el más eficaz planta natural utilizada tanto externa como internamente y son numerosos los beneficios que se derivan de esta maravillosa planta. Los beneficios para la salud del Aloe Vera se han propagado por todo el mundo.
Hoy en día, el Aloe Vera se cultiva comercialmente en diferentes partes del mundo para satisfacer la gran demanda de Aloe Vera. gel, jugo y látex que tienen variadas aplicaciones y usos en la cosmética, alimentación y medicina alternativa.
La planta de Aloe Vera se cultiva en áreas tropicales cálidas y no puede sobrevivir a temperaturas bajo cero. Agricultores en la India se enfrenta regularmente a problemas como la falta de lluvia, el bajo nivel del agua subterránea, la degradación del suelo, etc.
Dr. Indu Mehta Department of History Kumaun University, Nainital, Uttarakhand (India) Corresponding Author: Dr. Indu Mehta